
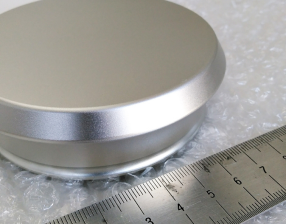
Machined parts are bead blasted with glass beads to achieve a uniform, matte texture and eliminate machining marks.
Bead blasting is a type of abrasive blasting process that uses spherical glass beads as the blasting media. Compared with traditional sandblasting, bead blasting is gentler, producing a satin matte finish without significant material removal — perfect for parts that require a clean and attractive appearance.




Utilizes rotating cutting tools for high-precision machining of flat surfaces, curves, and complex parts, ideal for mold making, aerospace, and automotive industries.

Uses rotating workpieces and cutting tools for efficient machining of cylindrical components, widely applied in shafts, discs, and precision parts manufacturing.

Enables multi-angle precision cutting, reducing setups and machining complex surfaces, perfect for high-end aerospace, medical devices, and precision mold manufacturing.



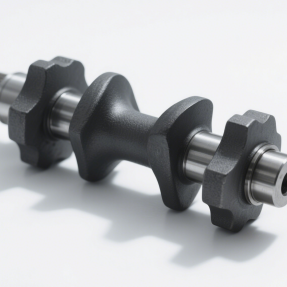
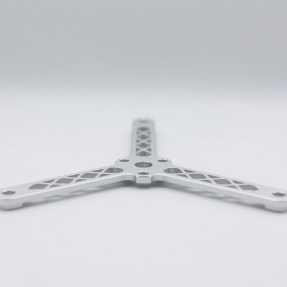

Cause: Inconsistent nozzle movement or unstable air pressure.
Impact: Visible differences in gloss or texture across the part surface.
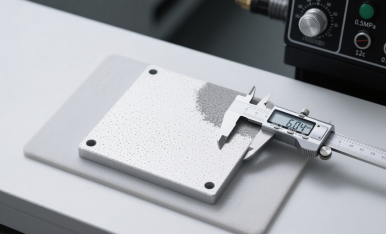
Cause: Excessive blasting time or high pressure.
Impact: Surface becomes too rough, minor dimensional changes may occur, potentially affecting tolerances.

Cause: Incomplete cleaning after blasting.
Impact: Remaining glass beads may cause surface defects during anodizing or coating.

Cause: Media not replaced on time or dirty recycling system.
Impact: Surface shows spots, stains, or color inconsistency.

Cause: Incorrect blasting angle or pressure.
Impact: Sharp edges or fine features become overly rounded, affecting assembly or function.
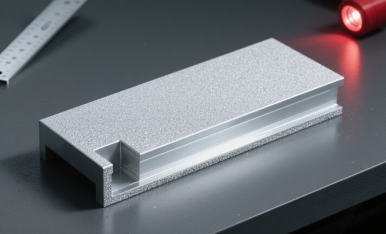
Cause: Spray angle cannot reach deep corners or blind spots.
Impact: Some areas keep their original gloss, resulting in a non-uniform appearance.
| 01 |
Degreasing & Cleaning
Removes oil, dust, and residues for a clean surface.
Typical Parameters:
Alkaline wash 50–70 °C, 5–10 min.
Standards:
In-house BB-SOP-01;
|
Standards:
In-house BB-SOP-01;
|
 |
| 02 |
Masking
Protects threads, bores, and critical areas from blasting.
Tools:
High-temp tape, silicone plugs, caps.
Standards:
In-house BB-SOP-02;
|
Standards:
In-house BB-SOP-02;
|
 |
| 03 |
Media Selection
Choose appropriate bead size (#80, #100, #120) based on desired surface
roughness.
Typical Media:
Glass beads, ceramic beads.
Standards:
In-house BB-SOP-03;
|
Standards:
In-house BB-SOP-03;
|
 |
| 04 |
Parameter Setup
Adjust blasting pressure, angle, and nozzle distance for uniform finish.
Typical Parameters:
60–90 PSI, 45–60° nozzle angle.
Standards:
In-house BB-SOP-04;
|
Standards:
In-house BB-SOP-04;
|
 |
| 05 |
Blasting Operation
Perform blasting in consistent sweeping motion to achieve satin finish.
Tools:
Pressure blaster, gloves, eye protection.
Standards:
In-house BB-SOP-05;
|
Standards:
In-house BB-SOP-05;
|
 |
| 06 |
Media Recycling
Filter and reuse media to maintain consistent surface quality.
Typical Process:
Cyclone separator, sieving.
Standards:
In-house BB-SOP-06;
|
Standards:
In-house BB-SOP-06;
|
 |
| 07 |
Final Cleaning
Blow off dust, check for embedded beads or contamination.
Tools:
Compressed air gun, visual inspection.
Standards:
In-house BB-SOP-07;
|
Standards:
In-house BB-SOP-07;
|
 |
| 08 |
Post-Process
Prepare part for next process (e.g., anodizing, coating, packaging).
Typical Processes:
Anodizing, powder coating, direct shipment.
Standards:
In-house BB-SOP-08;
|
Standards:
In-house BB-SOP-08;
|
 |




| Property | Typical Range |
| Surface Roughness (Ra) | 1.2–3.2 μm |
| Media | Glass beads (spherical) |
| Media Size | #80 / #100 / #120 / #150 |
| Air Pressure | 60–90 PSI (adjustable) |
| Best For | Aluminum, stainless steel, brass parts |







Send us your part files or design drawings. Our finishing experts will evaluate the geometry, surface requirements, and production scale to recommend the ideal Bead Blasting process for your CNC machined parts.